
Interpreting the Odds Ratio in Logistic Regression using SPSS YouTube
A binomial logistic regression (often referred to simply as logistic regression), predicts the probability that an observation falls into one of two categories of a dichotomous dependent variable based on one or more independent variables that can be either continuous or categorical.

2022 Odds Ratio 中文 Interpreting Odds Ratio For Multinomial Logistic Regression Using SPSS
This video demonstrates how to interpret the odds ratio for a multinomial logistic regression in SPSS. In this example, there are two independent variables:.
Use and Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio in SPSS Accredited Professional Statistician For Hire
Step #1: You need to interpret the results from your assumption tests to make sure that you can use ordinal regression to analyse your data. This includes analysing: (a) the multiple linear regression that you will have had to run to test for multicollinearity ( Assumption #3 ); and (b) the full likelihood ratio test comparing the fitted.
Use and Interpret ChiSquare in SPSS
The odds ratio for a feature is a ratio of the odds of a bike trip exceeding 20 minutes in condition 1 compared with the odds of a bike trip exceeding 20 minutes in condition 2. Positive odds ratios indicate that the event is more likely to occur, whilst negative odd ratios indicate the event is less likely to occur.

How to Compute an Odds Ratio Using SPSS YouTube
For many users though, understanding the differences between odds ratios and relative risk values can be a challenge. Moreover, in SPSS Statistics, deciphering these values correctly can be confusing as the variable arrangement and category order affect the calculation of the ratios and their interpretation.

Data analysis of CaseControl study using SPSS Odds Ratio logistic regression YouTube
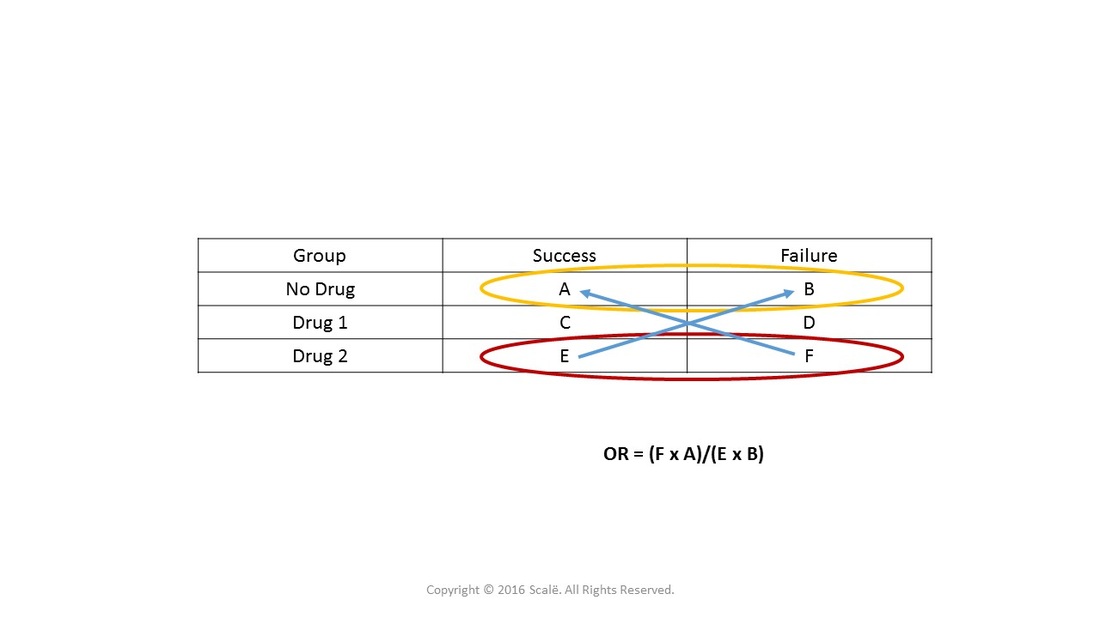
An odds ratio is a relative measure of effect, which allows the comparison of the intervention group of a study relative to the comparison or placebo group. So when researchers calculate an odds ratio they do it like this: The numerator is the odds in the intervention arm The denominator is the odds in the control or placebo arm = Odds Ratio (OR)

Odds ratio SPSS YouTube
This video demonstrates how to calculate odds ratio and relative risk values using the statistical software program SPSS.SPSS can be used to determine odds r.

ODDS RATIO O RAZÓN DE MOMIOS EN SPSS. PASO A PASO. EXPLICACIÓN E INTERPRETACIÓN. FÁCIL. YouTube
March 2, 2020 by Zach How to Interpret Odds Ratios In statistics, probability refers to the chances of some event happening. It is calculated as: PROBABILITY: P (event) = (# desirable outcomes) / (# possible outcomes) For example, suppose we have four red balls and one green ball in a bag.
Epidemiologic studies in SPSS Khi square test, odds ratio, relative risk and interpretation
Introduction Let's begin with probability. Let's say that the probability of success is .8, thus p = .8 Then the probability of failure is q = 1 - p = .2 The odds of success are defined as odds (success) = p/q = .8/.2 = 4, that is, the odds of success are 4 to 1. The odds of failure would be odds (failure) = q/p = .2/.8 = .25.

How to estimate odds ratios with zeros when running binary logistic regression in SPSS?
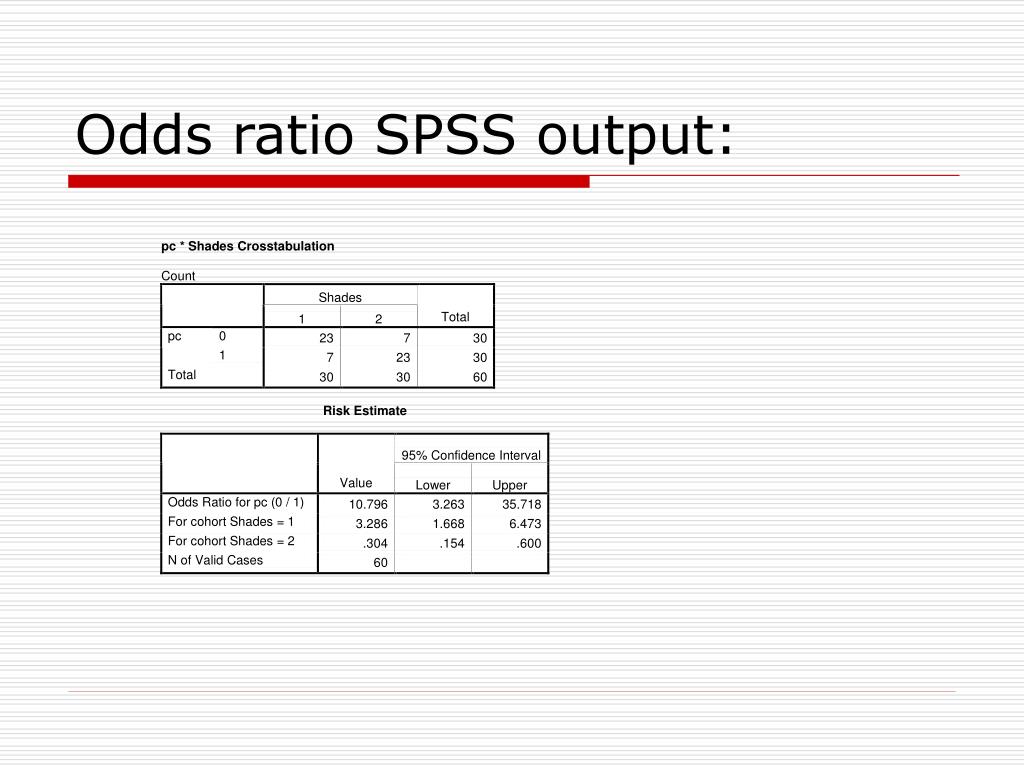
See the interpretations of the relative risk ratios below for examples. In general, if the odds ratio < 1, the outcome is more likely to be in the referent group. For more information on interpreting odds ratios, please see How do I interpret odds ratios in logistic regression? and Understanding RR ratios in multinomial logistic regression.
Use and Interpret ChiSquare in SPSS
The odds of success are defined as the ratio of the probability of success over the probability of failure. In our example, the odds of success are .8/.2 = 4. That is to say that the odds of success are 4 to 1. If the probability of success is .5, i.e., 50-50 percent chance, then the odds of success is 1 to 1.

Measuring Relative Risk of an Event Odds Ratio in SPSS YouTube
An odds ratio (OR) calculates the relationship between a variable and the likelihood of an event occurring. A common interpretation for odds ratios is identifying risk factors by assessing the relationship between exposure to a risk factor and a medical outcome. For example, is there an association between exposure to a chemical and a disease?
SPSS Video 10 Obtaining Odds Ratio & Relative Risk In SPSS YouTube
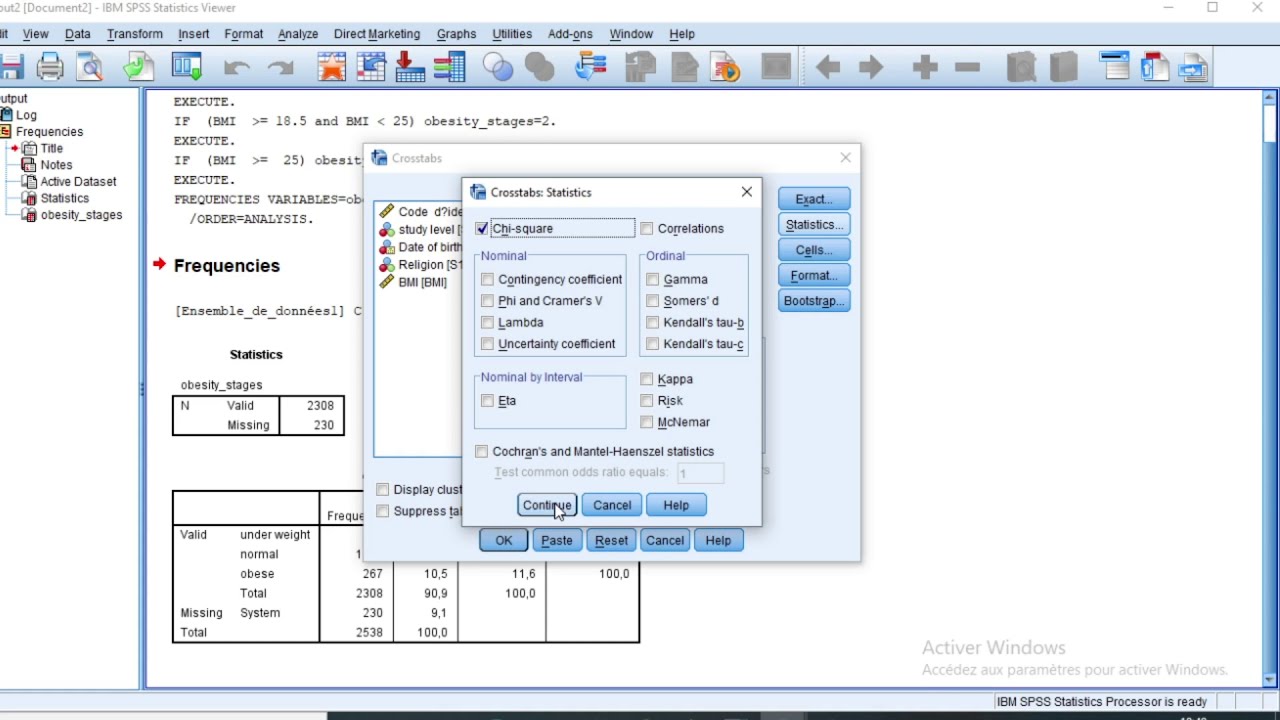
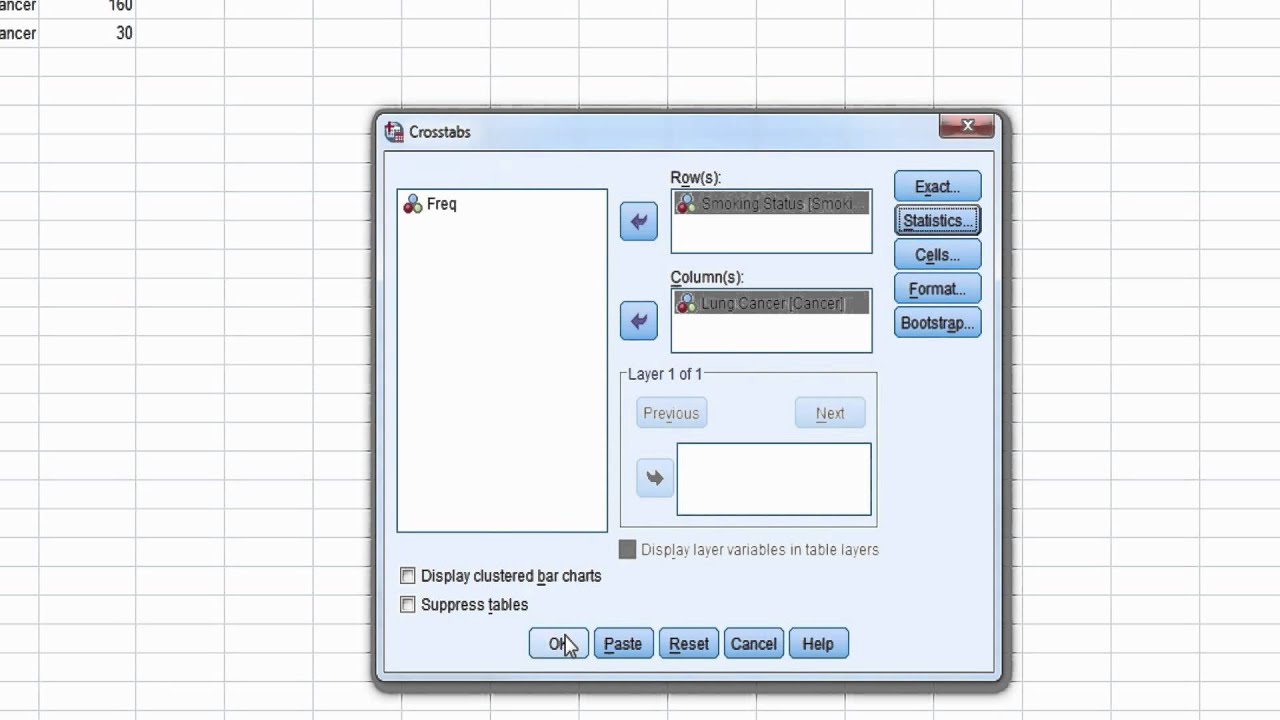
The steps for conducting an unadjusted odds ratio in SPSS 1. The data is entered in a between-subjects fashion. 2. Click A nalyze. 3. Drag the cursor over the R egression drop-down menu. 4. Click Binary Lo g istic. 5. Click on the dichotomous categorical outcome variable to highlight it. 6.

odd ratio and relative risk in theory and application in SPSS YouTube
f. Total - This is the sum of the cases that were included in the analysis and the missing cases. In our example, 200 + 0 = 200. Unselected Cases - If the select subcommand is used and a logical condition is specified with a categorical variable in the dataset, then the number of unselected cases would be listed here.
Use and Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio in SPSS Accredited Professional Statistician For Hire
Logistic regression is a technique for predicting a dichotomous outcome variable from 1+ predictors. Example: how likely are people to die before 2020, given their age in 2015? Note that "die" is a dichotomous variable because it has only 2 possible outcomes (yes or no).
PPT Repeated Measures PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3645207
Click the Analyze tab, then Regression, then Binary Logistic Regression: In the new window that pops up, drag the binary response variable draft into the box labelled Dependent. Then drag the two predictor variables points and division into the box labelled Block 1 of 1. Leave the Method set to Enter. Then click OK. Step 3. Interpret the output.